Minimally Invasive Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery (MICS CABG) is an advanced surgical technique used to treat coronary artery disease (CAD) with fewer complications and a faster recovery time compared to traditional open-heart surgery. Unlike conventional bypass surgery, which requires a large incision in the chest and splitting of the breastbone (sternotomy), MICS CABG is performed through a small incision on the left side of the chest, typically between the ribs. This approach eliminates the need for cutting bones, reduces pain, minimizes scarring, and allows for a quicker return to normal activities.
The procedure is performed using specialized instruments and advanced surgical techniques, ensuring precision and safety. MICS CABG is ideal for selected patients who require a bypass for one or more blocked arteries, especially those who are not candidates for percutaneous coronary intervention (stents). The benefits include reduced hospital stays, lower infection risks, minimal blood loss, and a shorter recovery period.
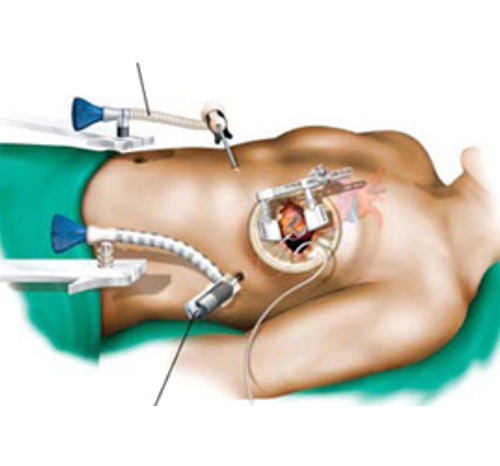
This technique is gaining popularity in major hospitals worldwide, particularly in advanced cardiac centers where experienced surgeons specialize in minimally invasive heart surgery. Patients considering MICS CABG should consult with a cardiac surgeon to determine if they are suitable candidates for this procedure.
